First Introduction
Detecting pheromones and chemical cues that affect social and reproductive activities depends critically on the auxiliary olfactory system in mice. In mice, mating, territoriality, and aggression all depend on this particular sensory system—unique from the main olfactory system. Knowing its structure and purpose helps one to have important understanding of mammalian sensory processing and communication.
Together with often asked questions regarding its importance in research and behavior, this guide will discuss the anatomy, function, and relevance of the accessory olfactory system (AOS) in mice.
Describes the Accessory Olfactory System
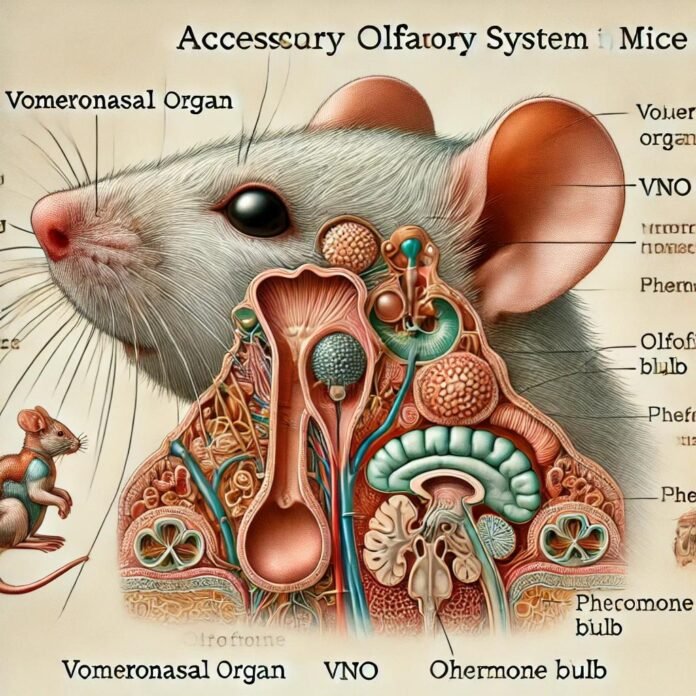
A secondary chemosensory system, the accessory olfactory system picks pheromones—chemical signals sent between members of the same species—that provide information between individuals. It mostly consists of the:
- Vomeronasal Organ (VNO): Found at the base of the nasal cavity, this specialized structure senses pheromonal stimuli.
- Accessory Olfactory Bulb (AOB): Processes pheromonal signals and distributes information to several brain areas engaged in social behaviors.
Unlike the primary olfactory system, which detects a broad spectrum of airborne smells, the AOS is especially adapted to non-volatile pheromones that demand direct touch or close-range detection.
Mammalian Accessory Olfactory System Anatomy and Function
1. Vomeronasal Organ (VNO)
The main AOS sensory organ is the VNO. It boasts two separate populations of sensory neurons:
- V1R-expressing neurons: Detect minute, water-soluble pheromones.
- V2R-expressing neurons: React to larger, protein-based pheromones.
Before getting to higher brain centers, these neurons send signals to the accessory olfactory bulb where pheromone information is processed.
2. Accessory Olfactory Bulb (AOB)
The VNO inputs the AOB, which then handles pheromonal signals. Because it specializes in identifying social and reproductive cues, the AOB differs from the main olfactory bulb (MOB) in both function and organization.
3. Behavioral Reactions and Neural Pathways
Pheromone signals following processing in the AOB are sent to brain areas including:
- Medial amygdala: Controls aggressiveness and reproduction.
- Hypothalamus: Regulates hormonal responses to pheromonal signals.
Mice using this pathway can recognize and react to conspecifics in ways that affect territoriality, mating, and dominance.
Accessory Olfactory System: Function in Mouse Behavior
1. Reproduction and Mating
Recognizing sexual cues and enabling mating behaviors depend on the AOS. Whereas females react to male-specific pheromones to induce reproductive readiness, male mice use pheromones to find receptive females.
2. Territory and Social Behavior
Pheromones help mice establish territory and dominance. Male mice produce pheromonal signals meant to discourage competition and attract potential mates.
3. Parental and Kin Recognition
The AOS facilitates kin recognition, enabling mice to distinguish between relatives and non-relatives, preventing inbreeding and promoting social group behaviors.
4. Defensive Actions and Aggression
Especially in males competing for mates or territory, pheromones sensed by the AOS might trigger aggressive responses.
AOS Research and Biomedical Applications
1. Understanding Mammalian Communication
Researching the AOS in mice helps one to understand how mammals use chemical signals to communicate, influencing topics such as genetics, animal behavior, and neurology.
2. Human Sensory Research Implications
Although humans lack a functional vomeronasal organ, studies on mice assist researchers in understanding how pheromones could still influence subconscious human behavior.
3. Potential for Disease Research
The AOS has been linked to neurodevelopmental disorders, particularly autism spectrum disorders (ASD), where altered social communication is a core symptom. Studies on the AOS could help reveal mechanisms behind these disorders.
FAQs on Mice’s Accessory Olfactory System
READ ABOUT-What Smells Do Mice Hate? Effective Natural Repellents to Keep Mice Away
1. How does the accessory olfactory system differ from the main olfactory system?
Whereas the AOS specializes in detecting pheromones that transmit social and reproductive information, the primary olfactory system detects general smells via airborne molecules.
2. If the accessory olfactory system is compromised, can mice still detect pheromones?
Mice with a damaged AOS may struggle to identify social cues, leading to altered mating, aggression, and territorial behavior.
3. Do all mammals have an accessory olfactory system?
While many mammals—including certain primates and rodents—have a functional AOS, humans possess a vestigial vomeronasal organ that is essentially non-functional.
4. How do researchers study the accessory olfactory system in mice?
Researchers investigate how the AOS processes pheromonal signals using methods such as gene knockout models, electrophysiological recordings, and behavioral tests.
5. How does the AOS contribute to mouse aggression?
Particularly in male mice competing for territory or mates, the AOS detects pheromones that trigger aggressive behavior. The hypothalamus and medial amygdala mediate this response.
Final Thought
The accessory olfactory system in mice is essential for their social and reproductive activities, enabling them to recognize and respond to pheromonal signals. Understanding the AOS allows scientists to gain deeper insights into mammalian communication, neural processing, and its potential applications in biomedical research.
The AOS remains a crucial model for comprehending sensory processing and its impact on behavior. Whether you’re interested in neuroscience or a researcher, studying the AOS provides fascinating perspectives on the complex world of chemical communication in mammals.